This is What Happens to Your Body When You Don’t Get Enough Sleep
Advertisement

It’s time to put sleep on your priority list of the day
Sleep deprivation makes you sick. You might know it clearly - If you don’t sleep, you don’t feel good. However, it seems to become the norm that most of us choose to sacrifice hours in bed, and distracted by working, chores, social media and so many other things, instead of sleeping. It all turns out that, we are taking the steep cost of insufficient sleep – our health.
There’s a reason poor sleep makes you feel so terrible. It can have a negative effect on nearly every part of the body. Numerous studies have shown that people who don’t get enough rest have a greater risk of health problems and diseases.
How much sleep do you actually need?

Many of us are lacking when it comes to it. Researchers have found that 30% of our population are not getting at less than seven hours of sleep per night. This means 1 in 3 adults is sleep deprived. Now that we know sleep is so important to our overall health. How much sleep do we need on earth in order to get these benefits?
According to the National Sleep Foundation, each age group is recommended to have a targeted sleep number as below:
• Adults, 65+ years: 7 to 8 hours.
• Adults, 26 to 64 years: 7 to 9 hours.
• Young adults, 18 to 25 years: 7 to 9 hours.
• Teenagers, 14 to 17 years: 8 to 10 hours.
Here's what happens when you don't get enough sleep, including the head-to-toe effects on your body.
Consequences of Sleep Deprivation
The effects of sleep deprivation can be serious and far-reaching.
Obesity:

Numerous studies have found that people who slept six hours a night or fewer were four times likelier to be obese. Not getting enough sleep alters hormone levels in our body, and leads to hunger and high-calorie food cravings. Additionally, insufficient sleep can impair your metabolism of food and energy. Obesity, in turn, also contributes to sleep issues. It is a detrimental cycle.
Diabetes:

Researches also show direct correlation between a higher risk of type 2 diabetes and lack of sleep. If you already are a diabetics, poor sleep could make it harder to manage.
Lack of sleep can cause your body to release less insulin after eating. Insulin is a hormone produced in the pancreas that controls your blood sugar. When insulin doesn't work as effectively, too much glucose can stay in your blood, increasing your risk of developing type 2 diabetes. In addition, poor sleep affects our hormone levels, making us crave foods and drinks that are high in sugars and carbohydrates. This can also contribute to the development of type 2 diabetes overtime.
Increase risks of heart attack:
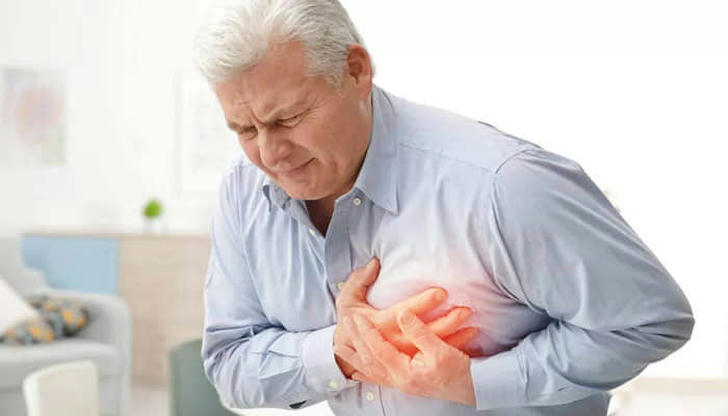
According to the American College of Cardiology, people who sleep less time have a 20% higher risk of heart disease. Sleep is a necessary time for the body to recover. When deprived, atherosclerosis can be triggered to happen, the buildup of plaque in arteries that restricts blood flow and thus, leads to heart disease. In addition, chronic lack of sleep may bring your blood pressure spikes, and put you in higher risks of stroke.
Memory impairment:

You may become forgetful because of poor sleep. When sleeping, the brain works to retain new information and memories. Your memory gets worse with the time you sleep each night. So sleep deprivation can impact attention, memory and information process in a negative way.
Weaker immune system:
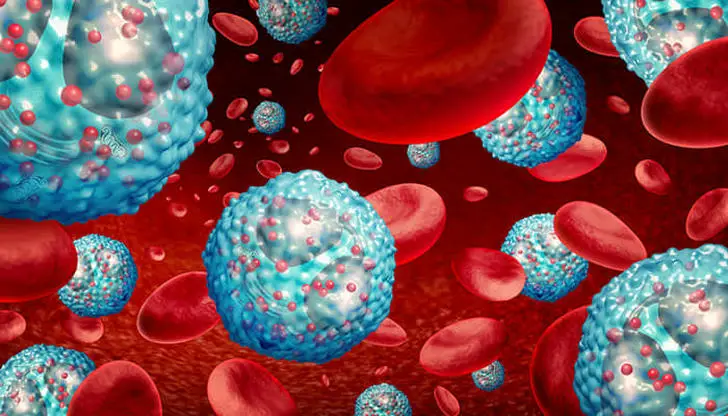
The immune system is critical to overall health. Sufficient sleep help boosts immune memory. When you sleep, components of your immune system interact to enhance your immune system's memory to recognize and respond to harmful antigens. Sleeping less than 6-7 hours a day has been linked to weakening, even disrupting immune system. Studies have shown that people who don't get enough sleep are more likely to get sick after being exposed to the virus.
Aging:

Sleep deprivation may cause you to feel older than you are. More studies have found that people who have a poor sleep is likelier to notice an increase in fine lines, uneven pigmentation and reduced elasticity in their skin. Simply put, they look older than their actual years would indicate. Our skin often repair and rejuvenate in the time we fall asleep at night. When not getting enough sleep, damages will be caused irreversibly to collagen in your skin. As collagen breaks down, your skin is no longer as firm and smooth. Along with collagen decrease, you can also experience dry skin because lack of sleep also lowers your PH levels.
If you are struggling with sleep, it is recommended that you first try to prioritize rest and practice regular sleep hygiene, remove electronic devices from your bedroom, make sure your bedroom is quiet, dark, relaxing and the right temperature.