Unveiling the Shadows: Navigating Social Anxiety in the Realm of Mental Illness
Advertisement

Social anxiety is a common mental health condition characterized by intense fear and discomfort in social situations. It affects millions of people worldwide, often leading to significant distress and impairment in various areas of life. When combined with an existing mental illness, such as depression, bipolar disorder, or schizophrenia, social anxiety can exacerbate the challenges individuals face. This essay explores the ways in which social anxiety affects individuals with mental illness, highlighting the additional burdens they may experience.
Isolation and Withdrawal

Social anxiety can amplify feelings of isolation and withdrawal for individuals with mental illness. The fear of being judged, ridiculed, or misunderstood may discourage them from participating in social activities, even when they desire social connection. This isolation can exacerbate symptoms of their existing mental illness and hinder their ability to develop meaningful relationships and support networks.
Impaired Treatment and Recovery

Receiving adequate treatment and support is crucial for individuals with mental illness. However, social anxiety can interfere with seeking help and engaging in therapy. The fear of being in the spotlight, interacting with strangers, or expressing emotions openly may prevent individuals from accessing the resources they need. As a result, their mental health condition may worsen, hindering their overall recovery process.
Negative Self-Perception and Stigma

Individuals with mental illness already contend with societal stigma and self-doubt. Social anxiety can intensify these negative perceptions and beliefs about oneself. The fear of social judgment can lead to distorted self-perception, low self-esteem, and feelings of inadequacy. Consequently, individuals may become trapped in a cycle of self-criticism, further impeding their mental well-being and recovery.
Interpersonal Difficulties

Social anxiety can create significant challenges in establishing and maintaining relationships for individuals with mental illness. Difficulty initiating conversations, fear of rejection, or excessive self-consciousness may hinder their ability to form connections with others. These interpersonal difficulties can contribute to a sense of loneliness and isolation, further impacting their mental health.
Impact on Daily Functioning

Social anxiety can affect various aspects of daily functioning for individuals with mental illness. Attending school or work may become daunting tasks due to anxiety about social interactions. The fear of scrutiny or embarrassment can impair concentration, productivity, and overall performance. Consequently, individuals may face additional challenges in their educational or professional pursuits, potentially leading to a sense of frustration and diminished self-worth.
Social anxiety has a profound impact on individuals with mental illness, exacerbating their struggles and impeding their recovery. The interplay between social anxiety and pre-existing mental health conditions creates a complex web of challenges that can hinder social connections, treatment-seeking behaviors, and daily functioning. Recognizing the significant burden social anxiety places on these individuals is essential for providing appropriate support and interventions. By addressing social anxiety alongside existing mental health concerns, it becomes possible to foster an environment of understanding, acceptance, and empowerment, enabling individuals to navigate their unique challenges and achieve improved overall well-being.
Overcoming or transcending social anxiety in individuals with mental illness can be a gradual and personalized process. Here are some possible ways to address and alleviate the difficulties associated with social anxiety:
Seek Professional Help

Consulting a mental health professional, such as a therapist or psychiatrist, can provide valuable guidance and support. They can help individuals develop coping strategies, challenge negative thought patterns, and implement evidence-based therapies like cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) or exposure therapy.
Medication
In some cases, medication prescribed by a psychiatrist may be beneficial in reducing the symptoms of social anxiety and underlying mental illness. It is important to consult a healthcare professional to determine the appropriateness of medication and discuss potential benefits and side effects.
Gradual Exposure

Gradual exposure to feared social situations can be an effective way to desensitize oneself and build confidence. By starting with small, manageable steps and gradually increasing the level of exposure, individuals can learn to cope with anxiety-provoking situations and challenge their fears.
Support Groups

Participating in support groups or joining community organizations can provide a safe and understanding environment to practice social interactions. Meeting individuals who share similar experiences can help reduce feelings of isolation and provide opportunities for mutual support and encouragement.
Self-Care Practices

Engaging in self-care activities, such as exercise, meditation, mindfulness, and relaxation techniques, can help manage anxiety symptoms. Taking care of one's physical and mental well-being can enhance overall resilience and reduce the impact of social anxiety.
Social Skills Training

Participating in social skills training programs or workshops can provide individuals with practical tools to navigate social interactions more confidently. These programs can teach communication techniques, assertiveness training, and effective coping strategies in social settings.
Building a Supportive Network
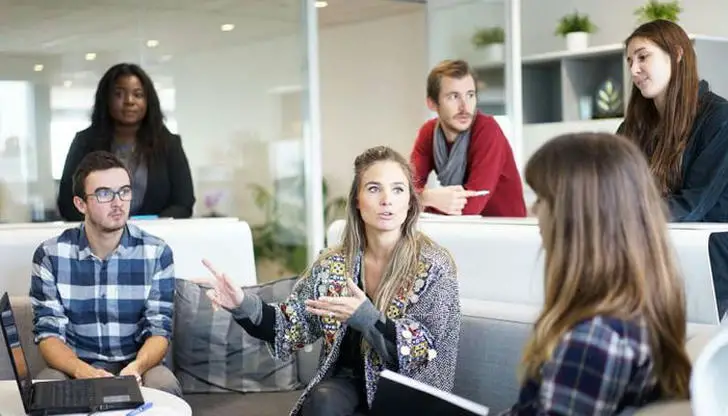

Surrounding oneself with understanding and supportive individuals can create a positive social environment. Connecting with friends, family, or support groups who are empathetic and accepting can help individuals feel more comfortable and less judged in social situations.
Challenge Negative Thoughts

Identifying and challenging negative thoughts and beliefs related to social anxiety can help individuals reframe their thinking. Engaging in cognitive restructuring techniques, such as questioning irrational beliefs or replacing negative thoughts with more realistic and positive ones, can contribute to a more balanced perspective.
Self-Reflection and Acceptance

Engaging in self-reflection and cultivating self-acceptance can be empowering. Embracing strengths, acknowledging progress, and accepting imperfections can contribute to building self-confidence and reducing the fear of social judgment.
Patience and Persistence

Overcoming social anxiety is a journey that requires patience and persistence. It is important to remember that progress may be gradual and setbacks can occur. Celebrating small victories and maintaining a positive mindset can help individuals stay motivated on their path to overcoming social anxiety.
It is crucial to note that everyone's experience with social anxiety and mental illness is unique. Therefore, it is essential to tailor these strategies to individual needs and seek professional guidance when necessary. With time, support, and appropriate interventions, individuals can gradually overcome or transcend the difficulties associated with social anxiety and experience improved well-being.